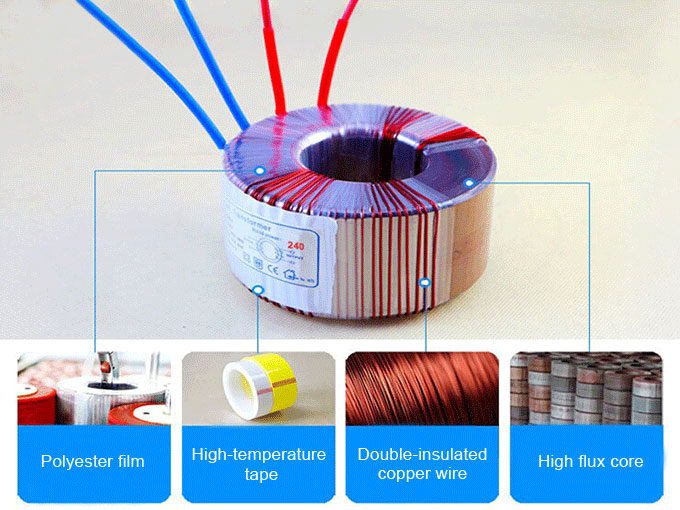
How to Determine the Voltage Converter Insulation Performance
The insulation performance determines the quality of the voltage converter.
1. Polyester film
Voltage converters in the production process will use polyester film as a package on core, semi-finished products and finished products, which is mainly to enhance the insulation effect. For example: When the voltage converter overload or audio amplifier instantaneous over-current causes voltage converter over-heat, the polyester film is no doubt to ensure the insulation safety for its high temperature characteristics.
2. Double-insulated copper wire
Voltage converter is using the double-insulated copper wire. The wire core is purple-red copper, which has good mechanical strength and excellent toughness.
3. High-temperature tape
The high-temperature tape used in the voltage converter has excellent electrical properties of high insulation, high temperature, low electrolysis, good mechanical properties. It further improves the insulation properties of voltage converters.
In addition, the lead wire of the voltage converter adopts UL certification. It has the outstanding advantages of cold resistance and high temperature resistance. The glass fiber bushing on the lead wire of the voltage converter also has extremely high electric strength. Voltage converter primary and secondary are spaced apart with good mechanical strength and electrical strength green shell paper. The whole system has strong insulation properties.
Some data of voltage converter:
In practical applications, after the temperature of use is determined, it tends to use at least the same level or higher insulation materials to improve the life of the voltage converter. Commonly used insulation class is B-class voltage converter, its internal insulation material is often F-class. The other is generally to improve the service life, often require advanced insulation requirements, with a low level to assess. For example, the common F-class insulation transformer, with B-level assessment, that is, the temperature rise can't exceed 120℃ (10℃ left as margin, in order to avoid the voltage converter due to process instability caused by individual temperature rise).
1. Polyester film
Voltage converters in the production process will use polyester film as a package on core, semi-finished products and finished products, which is mainly to enhance the insulation effect. For example: When the voltage converter overload or audio amplifier instantaneous over-current causes voltage converter over-heat, the polyester film is no doubt to ensure the insulation safety for its high temperature characteristics.
2. Double-insulated copper wire
Voltage converter is using the double-insulated copper wire. The wire core is purple-red copper, which has good mechanical strength and excellent toughness.
3. High-temperature tape
The high-temperature tape used in the voltage converter has excellent electrical properties of high insulation, high temperature, low electrolysis, good mechanical properties. It further improves the insulation properties of voltage converters.
In addition, the lead wire of the voltage converter adopts UL certification. It has the outstanding advantages of cold resistance and high temperature resistance. The glass fiber bushing on the lead wire of the voltage converter also has extremely high electric strength. Voltage converter primary and secondary are spaced apart with good mechanical strength and electrical strength green shell paper. The whole system has strong insulation properties.

Some data of voltage converter:
- Insulation class for voltage converters: Class A, Class E, Class B, Class F, Class H
- Heat-resistant temperature (℃): 105 120 130 155 180
- Winding temperature rise limit (℃): 60 75 80 100 125
In practical applications, after the temperature of use is determined, it tends to use at least the same level or higher insulation materials to improve the life of the voltage converter. Commonly used insulation class is B-class voltage converter, its internal insulation material is often F-class. The other is generally to improve the service life, often require advanced insulation requirements, with a low level to assess. For example, the common F-class insulation transformer, with B-level assessment, that is, the temperature rise can't exceed 120℃ (10℃ left as margin, in order to avoid the voltage converter due to process instability caused by individual temperature rise).
Post a Comment:
You may also like:

With a Voltage Converter, you can convert
110v to 220v;
120v to 220v;
220v to 110v;
230v to 110v;
240v to 110v.
Note, voltage converters do NOT convert 50Hz to 60Hz, or 60Hz to 50Hz.
Featured Articles
What Happens When an Appliance is ...
 If the 110V appliance is connected to a 220V power supply, the power may quadruple at the moment the appliance switched on, and ...
If the 110V appliance is connected to a 220V power supply, the power may quadruple at the moment the appliance switched on, and ...
 If the 110V appliance is connected to a 220V power supply, the power may quadruple at the moment the appliance switched on, and ...
If the 110V appliance is connected to a 220V power supply, the power may quadruple at the moment the appliance switched on, and ...Automatic 220v to 110v Voltage ...
 As we know, electric voltage of some countries and regions is 220V. But in America, the electric voltage is generally 110V. When ...
As we know, electric voltage of some countries and regions is 220V. But in America, the electric voltage is generally 110V. When ...
 As we know, electric voltage of some countries and regions is 220V. But in America, the electric voltage is generally 110V. When ...
As we know, electric voltage of some countries and regions is 220V. But in America, the electric voltage is generally 110V. When ...Voltage Difference between US and UK
 Many people who travel to the United States found it difficult to use their electronic devices, because of different power supply ...
Many people who travel to the United States found it difficult to use their electronic devices, because of different power supply ...
 Many people who travel to the United States found it difficult to use their electronic devices, because of different power supply ...
Many people who travel to the United States found it difficult to use their electronic devices, because of different power supply ...